Structure Query Language (SQL) in DBMS
➺ The SQL name was SEQUEL later changed to SQL(Structure Query Language).
➺ SEQUEL is a short form of Simple English Query Language.
➺ It was developed by IBM(Dr. EF Codd) in 1970.
➺ SQL refers to Structure Query Language.
➺ SQL is a domain-specific language that works with only RDBMS.
➺ My SQL table name size is 64 characters.
➺ It is a Non-Procedural query language.
SQL commands
➺ A dbms allows user to organize, process and retrieve data from database.
➺ There are 5 types of SQL commands:-
1. Data Definition Language (DDL)
2. Data Manipulation Language (DML)
3. Data Control Language (DCL)
4. Transaction Control Language (TCL)
5. Constraints.
Data Definition Language (DDL)
➺ It defines structure of database. It describes definition of each data elements of database.
➺ Using DDL commands we can perform tasks related to data definition such as create, alter and drop schema object, grant and revoke privileges etc.
➺ For example:- Creating field name, field length, field type, etc.
Create
➺ Using create commands we can create a database.
Example:-
> create database aakash;
> use aakash;
> show database;
Alter
➺Using alter table command we can change a table such as add a column, delete a column, or modify a column.
Add new column :
> alter table aakash
add city char(20);
Change column name :
> alter table aakash;
change name studentname char(20);
Modify column (datatype):
> alter table aakash;
modify city char(40);
Delete Column:
> alter table aakash;
drop city char(40);
Truncate
➺ It deletes the data inside a table but not the table itself. it only deletes data from the table not the structure of the table.
> truncate table aakash;
Drop
➺Using the Drop command we can drop or delete a specific table from the database.
> drop table aakash;
Data Manipulation Language (DML)
➺ Using DML commands are used to manipulate data of database.
➺ Using this commands, we can insert, delete, and update, data in a table.
➺ It allows to perform tasks related to data manipulation such as retrieve, insert, select, delete and modification of data stored in a database.
Select
➺ Using select query we can show a record from specified the table.
* : Using * (stick) sign to show all fields from specifying table.
ex:- > select * from aakash
where id = 1;
> select id, name from aakash
where name ='akki';
Insert
➺ Using this command we can insert a new record to the table.
ex:- > insert into tablename values
> insert into aakash values
(1,'akki','reodar',24);
Update
➺ Using this command we can modify record data in a table.
ex:- > update aakash
set name = 'akki'
where name = 'modi';
Delete
➺ Using this command we can delete a record in the table.
ex:- > delete from akki
where id =1;
Data Control Language (DCL)
➺ DCL commands allows to give right and permission to the user. Using this commands we can perform operation such as grant and revoke rights in a database.
➺ DCL commands includes :- Grant, Revoke.
Grant
➺ It grants permission to the user by giving access right in a database such as select, execute, all, etc.
➺ Syntax :- Grant < privilege list > ON < relation, view > TO < user, role, public >.
Note: Privilege list -> select, insert, update, delete, all, execute.
ex:- > grant select ON bank To aakash;
> grant insert ON akki To aakash;
Revoke
➺ Removing access rights of the user in the database.
➺ Syntax :- Revoke
ex:- > revoke select ON bank To aakash;
> revoke insert ON akki To aakash;
Transaction Control Language (TCL)
➺ This commands allow you to manage and control the transaction (a transaction is one complete unit of work involving many steps).
➺ For ex:- making changes to databases permanently, creating savepoints, undoing changes to database permanently, setting properties for current transaction.
Commit
➺ Using the commit command all changes made are permanent.
ex:- > select * from aakash;
5 record show
> delete from aakash
where id = 2;
> commit ;
> select * from aakash;
4 record show
➺ By default My SQL has autocommit.
Note:- After deleting one record we used commit so after that change made in database in permanent.
Rollback
➺ It use as undo. using this command we can revert all last transaction after last commit.
> select * from aakash;
8 record shows
> delete from aakash
where id = 1;
> delete from aakash
where name = 'akki';
> select * from aakash;
6 record shows
> rollback;
Savepoint
➺ In, we create a point. using savepoint can rollback selected transaction to the point.
> update bank
set amt = amt + 500;
> select * friom aakash;
> savepoint A;
> Delete from bank
where id = 2;
> select * from bank
> savepoint B;
> delete from bank
where id = 3;
> select * from bank;
> rollback to savepoint
Constraints
➺ Sql Constraints is a condition or check applicable on field / set of fields.
Primary key
➺ It refers to a set of one or more attributes that can uniquely identified the tuples (rows) within the relation.
➺ Primary key is uesd to check fields to not make duplicate entry.
➺ ex:
> create table info
( id integer primary key,
Name char(20),
amt integer,
city char(20));
Foreign key (Reference key)
➺ A non-key attribute, whose values are derived from primary key of another table is known as foreign key.
➺ In RDBMS, we are creating relationship between two different tables using reference creating relationships as per specify fields.
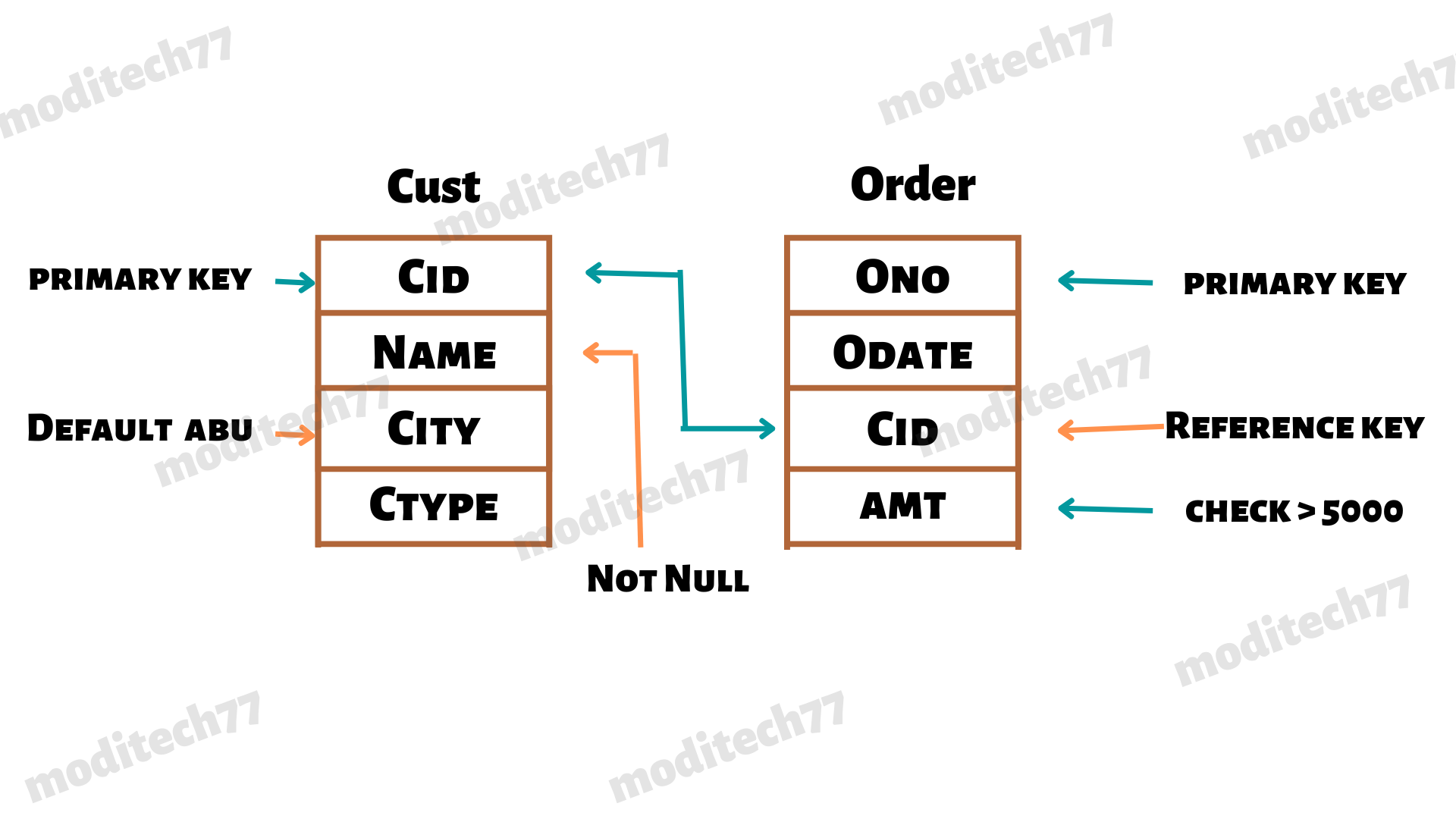
ex: > create table customer
( cid integer primary key,
Name char(20) not null,
city char(20) default 'abu',
ctype char(20));
> create table order
( ono integer primary key,
odate date,
cid integer reference customer(cid),
amt integer check amt > 5000);
Check
➺ Using check, we can check is specify values as per condition is true or not.
ex:- > create table info
( Sid integer,
name char(20),
Amt integer check(amt > 500));
Unique
➺ The Unique is used to check all values is available in particular column or not and two rows cannot hold same values.
ex:- > create table info
( Sid integer unique,
Fname char(20),
Sname char(20));
Default
➺ The default provides a default values to the columns when insert into statement.
➺ If we not add values to columns then default values will taken automatically in particular column.
ex:- > create table info
( id integer,
Name char(20),
Score default 80);
Not Null
➺ In Sql, By default a column called NULL. Not Null can be use with int, char, and where etc.
➺ If any column given Not null then colummn will not empty(null) must contains vlaues in column.
ex:- > create table info
( id integer not null,
Name char(20) not null);
Null
➺ By default, My Sql provides null value. It refer to no value in coulmn of table.
You might like this :-
○ ACID Properties in DBMS
○Normalization in DBMS
○RDBMS Introduction
○DBMS vs RDBMS